
The incubation period of an infectious disease is the time between infection and the onset of symptoms. This period varies depending on the type of virus, ranging from half a day to over a week for some viruses.2
Common symptoms of colds and flu include a runny or stuffy nose and sore throat. Other symptoms may include a mild cough, headache, and fever. An ordinary cold typically lasts fewer than ten days.1

On average, people experience two to five colds per year. Children, however, are the most frequently affected, catching 7 to 10 colds per year, with frequency generally declining with age.3
Recommendations to reduce the risk of infection from the common cold, flu, and other respiratory viruses:

References:
Both diseases are caused by different pathogens. While influenza viruses are responsible for a flu outbreak, the common cold can be triggered by over 200 different viruses.
Colds usually start gradually, whereas flu comes on suddenly and often involves a fever and muscle aches and pains.
Wet hair doesn’t cause a cold, it is caused by infection from common cold viruses.
However, if the immune system is already weak, becoming very cold can further weaken it. Wet hair in cold conditions can lead to a drop in body temperature which can have a negative effect on a weakened immune system, so it is best to avoid going into the cold with wet hair.
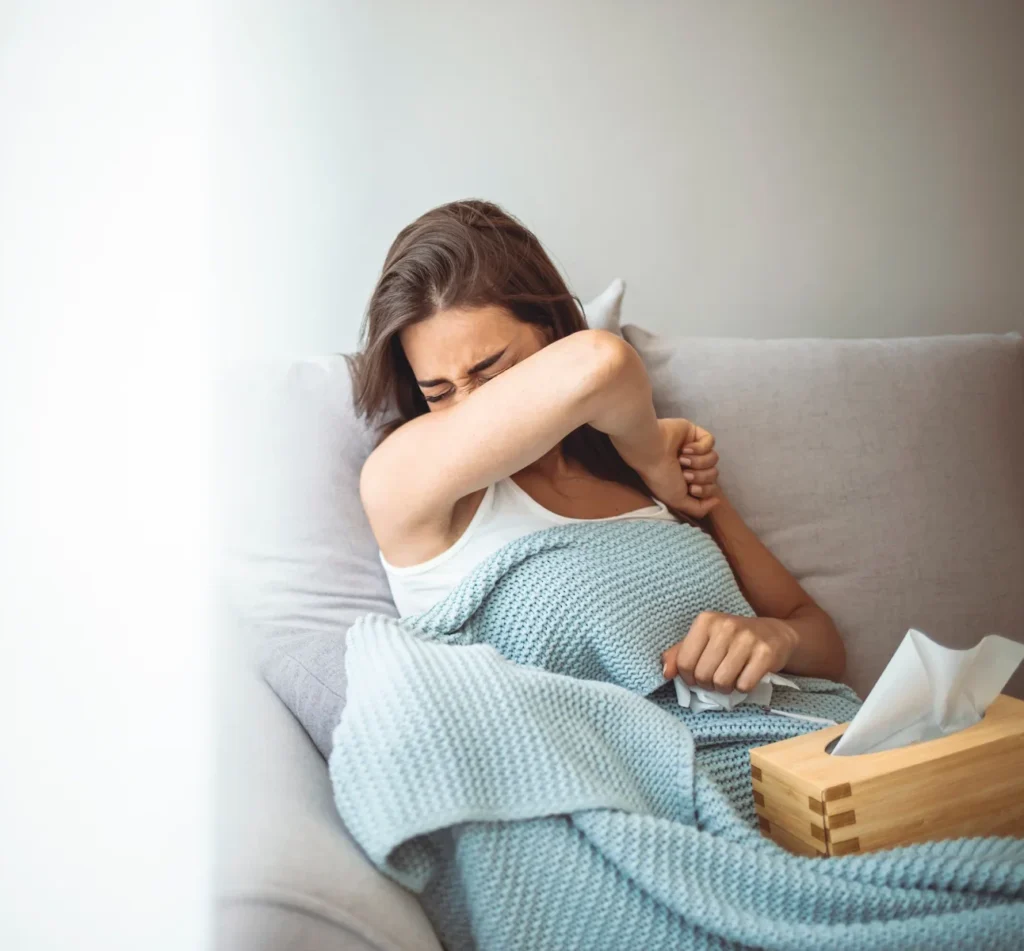
Many people still consider it polite to hold their hand over their mouth when coughing.
Anyone who coughs into their hand transmits an enormous number of viruses onto the palm of the hand. If they then touch objects, they increase the risk of infection for others immensely. So the advice is now to cough into the crook of the arm.
It appears that daily vitamin C has no real impact on catching a cold, although it may have a small positive effect on the duration of a cold, but only if it is taken as part of a daily routine. High doses of vitamin C once a cold has started have shown no consistent effect on duration or severity of common cold.